Kubernetes doesn’t have to be that way, you can use this simple cheat sheet to understand the basics.
Kubernetes Architecture Components
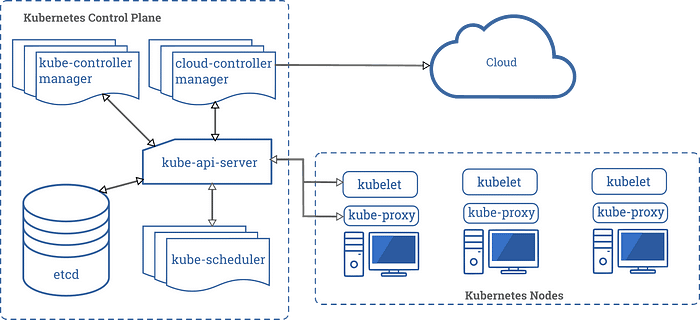
Master Node: The control plane of the cluster, responsible for managing the state of the cluster, scheduling and managing workloads, and providing a centralized configuration.
Worker Nodes: These are the machines (physical or virtual) that run your applications and services. Pods are scheduled on worker nodes, and the containers within those pods run on the worker nodes.
etcd: A distributed key-value store that provides a source of truth for the cluster state and configuration. The master node communicates with etcd to ensure the desired state of the cluster is maintained.
API Server: The front-end of the master node, responsible for serving the RESTful API used by all other components to interact with the cluster.
Controller Manager: Monitors the state of the cluster and makes changes as necessary to ensure the desired state is maintained.
Scheduler: Responsible for assigning pods to worker nodes based on available resources and constraints.
Kubelet: An agent that runs on each worker node, responsible for communicating with the master node and ensuring that containers are running as expected.
Container runtime: A software that is responsible for starting, stopping, and managing the containers. The most commonly used container runtime in Kubernetes is Docker.
Pods
Smallest building blocks for deploying and managing applications in a Kubernetes cluster. A pod can contain one or more containers, and all containers in a pod share the same network namespace
Display a list of pods in the cluster.
kubectl get podsShow detailed information about a specific pod.
kubectl describe pod pod_namePrint the logs of a specific pod.
kubectl logs pod_nameDelete a specific pod
kubectl delete pod pod_nameStart a pod with an nginx image
kubectl run nginx --image=nginxDeployments
Deployments allow you to define the desired state for a group of replicas (replica set) of your application, and the deployment controller makes sure that the actual state of the replicas matches the desired state. Deployments are a way to achieve multiple objectives, such as scaling, rolling updates, and rollbacks.
Nginx Sample Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80Services
Services enable communication between components of a microservices-based application, or between multiple applications. There are several types of Kubernetes services including ClusterIP, NodePort, LoadBalancer, ExternalName, and Headless services.
Create a ClusterIP service imperatively
The service will select pods belonging to the my-deployment deployment and expose them on port 80, forwarding traffic to target port 8080
kubectl expose deployment my-deployment --port=80 --target-port=8080 --name=my-service --type=ClusterIPCreate a NodePort service imperatively
The service will select pods belonging to the another-deployment deployment and expose them on port 80, forwarding traffic to target port 8080
kubectl expose deployment another-deployment --port=80 --target-port=8080 --name=my-service --type=NodePortCreate Cluster IP service declaratively
The service will select pods labelled with app: my-app and expose them on port 80, forwarding traffic to target port 8080.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: my-service
spec:
selector:
app: my-app
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 8080
type: ClusterIPStatefulSet
A StatefulSet is a type of Kubernetes resource that is used to manage stateful applications. Unlike a Deployment, which creates stateless replicas of a pod, a StatefulSet provides stable network identities and persistent storage to pods.
Each pod in a StatefulSet is created with a unique, persistent hostname that follows the pattern <statefulset-name>-<ordinal>. The ordinal is an index that is assigned to each pod in the order it was created, starting from 0.
StatefulSet Example Manifest
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: example-statefulset
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: example-statefulset
serviceName: example-service
replicas: 3
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: example-statefulset
spec:
containers:
- name: example-container
image: example-image
ports:
- containerPort: 80
volumeMounts:
- name: example-volume
mountPath: /data
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: example-volume
spec:
accessModes: [ "ReadWriteOnce" ]
resources:
requests:
storage: 1GiDaemonSet
A DaemonSet is a type of Kubernetes resource that ensures that exactly one pod is running on each node in a cluster. This is useful for running background tasks, such as logging agents or cluster-level storage daemons, that need to be running on every node.
DaemonSet Example Manifest
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: example-daemonset
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: example-daemonset
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: example-daemonset
spec:
containers:
- name: example-container
image: example-image
ports:
- containerPort: 80ReplicaSet
A ReplicaSet is a type of Kubernetes resource that ensures that a specified number of replicas of a pod are running in a cluster at any given time. The ReplicaSet automatically creates or deletes pods as necessary to maintain the desired number of replicas.
ReplicaSet Example Manifest
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: ReplicaSet
metadata:
name: example-replicaset
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: example-replicaset
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: example-replicaset
spec:
containers:
- name: example-container
image: example-image
ports:
- containerPort: 80Secrets
Kubernetes Secrets are a way to securely store sensitive information, such as passwords, tokens, and certificates, in a Kubernetes cluster. Secrets are stored as base64-encoded strings and are encrypted in etcd.
Secret Manifest Example
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: example-secret
type: Opaque
data:
example-username: YWRtaW4=
example-password: cGFzc3dvcmQ=Use Secret Value in Pod Manifest
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: example-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: example-container
image: example-image
env:
- name: EXAMPLE_USERNAME
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: example-secret
key: example-username
- name: EXAMPLE_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: example-secret
key: example-passwordConfigMaps
A ConfigMap is a Kubernetes resource that allows you to manage configuration data for your applications. You can store configuration data as key-value pairs in a ConfigMap and then reference it from your pods or other resources in the cluster.
ConfigMap Manifest
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: example-configmap
data:
example-key: example-valueUse ConfigMap value in a Pod Manifest
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: example-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: example-container
image: example-image
env:
- name: EXAMPLE_ENV_VAR
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: example-configmap
key: example-keyKubectl commands with examples
Retrieve information about one or many resources.
kubectl get podsGet detailed information about a resource
kubectl describe pod pod_nameRetrieve the logs of a container in a pod
kubectl logs pod_nameDelete a specific resource
kubectl delete pod pod_nameCreate a resource
kubectl create -f pod.yamlApply changes to an existing resource or create a new one if it doesn’t exist
kubectl apply -f pod.yamlExecute a command in a container
kubectl exec pod-name -- commandScale the number of replicas of a deployment
kubectl scale deployment deployment_name --replicas=5Forward a local port to a port in a pod.
kubectl port-forward pod_name 8080:80Edit a resource in place
kubectl edit pods pod_nameDisplay resource usage for one or many resources
kubectl top nodeMark a node as unschedulable, so that no new pods can be created on it
kubectl cordon node_nameMark a node as schedulable, allowing new pods to be created on it
kubectl uncordon node_nameSafely evict all pods from a node and mark it as unschedulable
kubectl drain node_nameSee Kubernetes version
kubectl version
Comments
Post a Comment